📄 02 - SET-1 (TDS problems) Part 2, p.10
⭐ Basic Concepts
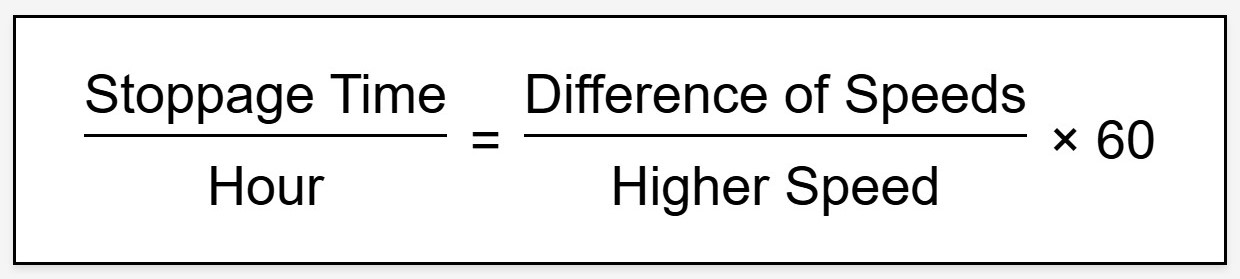
- In Stoppages Type, equate Speed and Time using Ratio Proportionate method.
- Start the sum from the R.H.S side by creating a fraction for stoppage Time/Hour.
- Then, create the same proportionate fraction on the L.H.S for Speed, and solve for the missing value.
⚡ Formula
A train travelled at an average speed of 100 kmph, stopping for 3 minutes after every 75 kms. How long did it take to reach its destination (600 km) from the starting point?
A) 6 hours 24 mins
B) 6 hours 21 mins
C) 6 hours 18 mins
D) 6 hours 15 mins
- Exclude the final stopping point, because the train does not wait for the 3‑minute interval after reaching its destination.

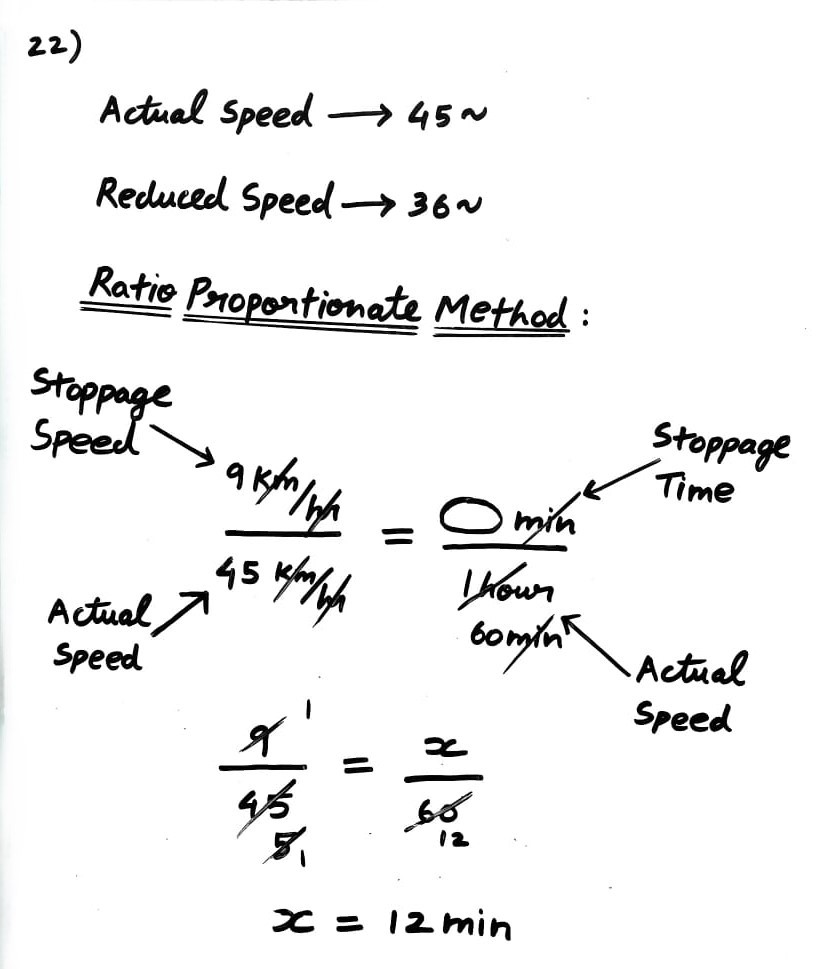
Excluding stoppages, the speed of a bus is 45 kmph and including stoppages, it is 36 kmph. How many minutes does the train stop per hour?
A) 10 mins
B) 12 mins
C) 15 mins
D) 20 mins
Method 1:
- In Stoppages Type, equate Speed and Time using Ratio Proportionate method.
- Start the sum from the R.H.S side by creating a fraction for stoppage Time/Hour.
- Then, create the same proportionate fraction on the L.H.S for Speed, and solve for the missing value.
Method 2:

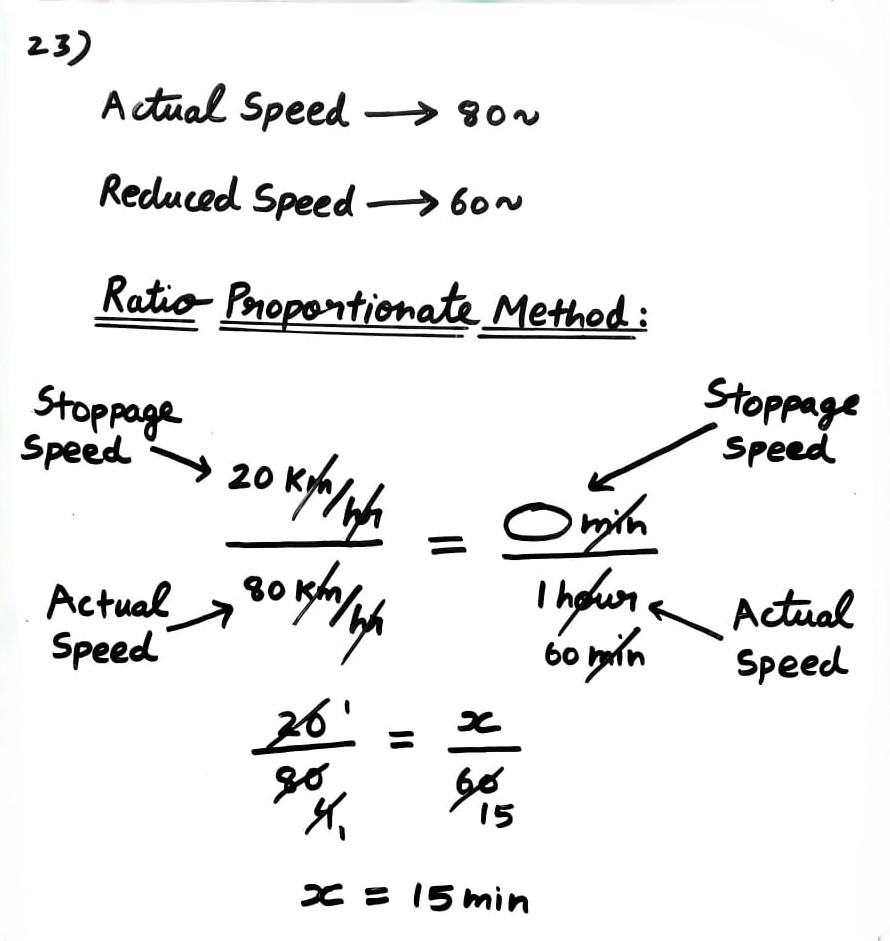
Without stoppages, a train travels a certain distance with an average speed of 80 kmph, and with stoppages, it covers the same distance at 60 kmph. What is the time in minutes per hour for which the train stops?
A) 15
B) 10
C) 20
D) 25
Method 1:
- In Stoppages Type, equate Speed and Time using Ratio Proportionate method.
- Start the sum from the R.H.S side by creating a fraction for stoppage Time/Hour.
- Then, create the same proportionate fraction on the L.H.S for Speed, and solve for the missing value.
Method 2:
