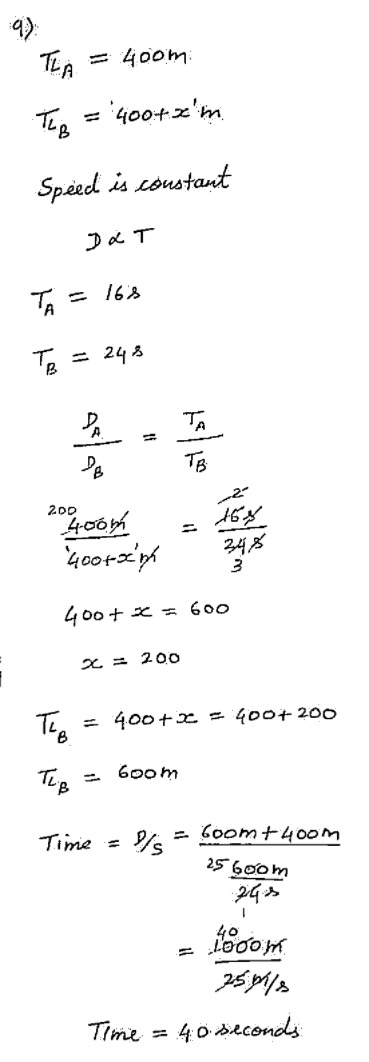📄 05 - SET-2 (Trains Basics), p.1
⭐ Basic Concepts
- In trains, distance "D" is the passing distance.
- In train problems, the length of the train should always be expressed in meters (m).
- Mnemonic → Department of Science and Technology.
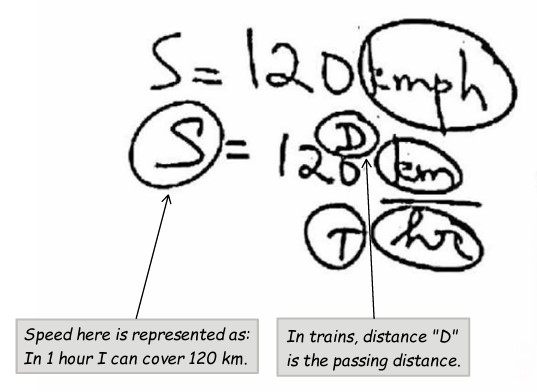
A train, 150m long passes a pole in 15 seconds. What is the speed of the train in km/hr?
(A) 20 km/hr
(B) 24 km/hr
(C) 10 km/hr
(D) 36 km/hr
(E) 38 km/hr
- To convert from a larger unit to a smaller unit, use a fraction with a smaller numerator (e.g., km/h to m/s → multiply by 5/18).
- To convert from a smaller unit to a larger unit, use a fraction with a larger numerator (e.g., m/s to km/h → multiply by 18/5).
A train crosses an 80m long platform in 30 seconds. If the speed of the train is 4 m/sec, what is the length of the train?
(A) 40m
(B) 55m
(C) 80m
(D) 60m
(E) 50m
A 240 m long train crosses a platform twice its length in 40 seconds. What is the speed of the train?
(A) 6 m/sec
(B) 28 m/sec
(C) 18 m/sec
(D) 16 m/sec
(E) 20 m/sec
A train 200 m long takes 10 seconds to pass a standing man. Find the time taken by the train in crossing a railway platform of 260 m in length.
(A) 23 seconds
(B) 13 seconds
(C) 26 seconds
(D) 36 seconds
(E) 20 seconds
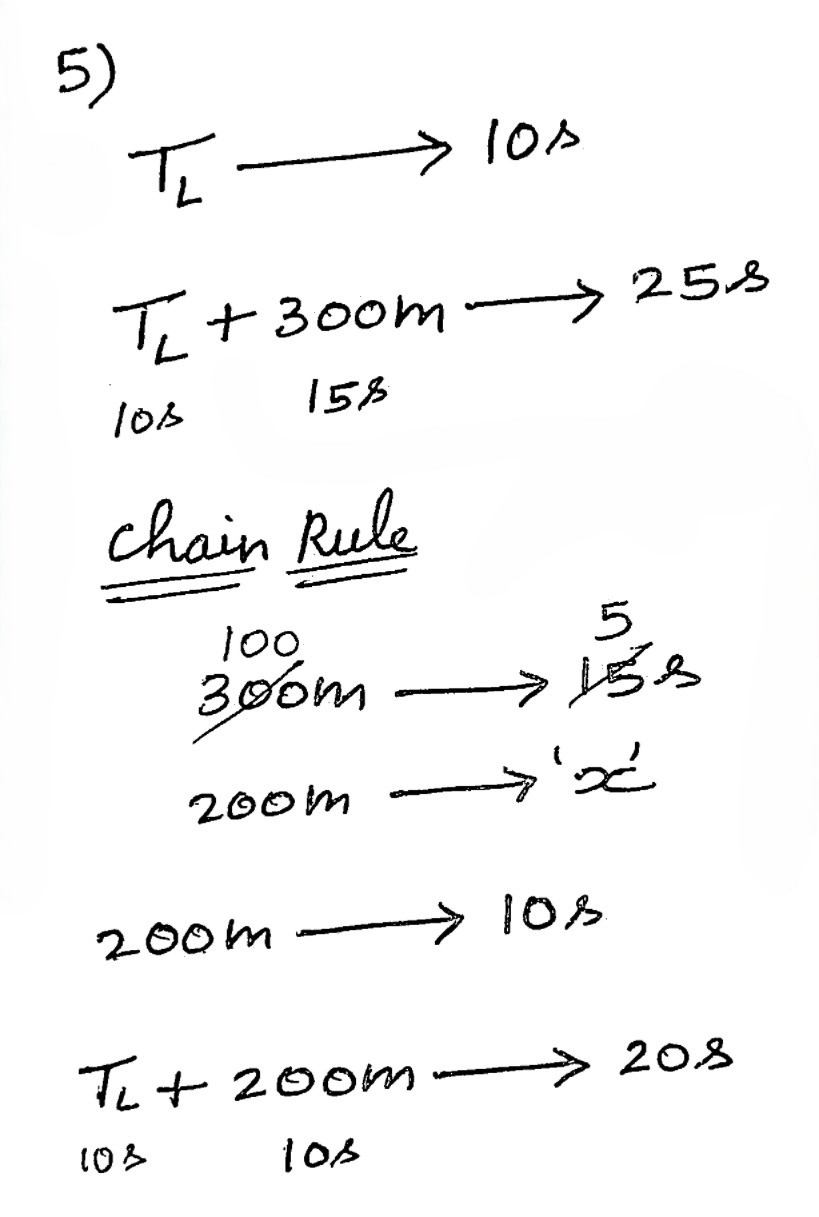
Use the Chain Rule to relate Distance and Time proportionally using Speed, and calculate the unknown Time.

A train crosses a pole and bridge 300 m long in 10 seconds and 25 seconds, respectively. How long will the train take to cross a 200 m long platform?
(A) 10 seconds
(B) 18 seconds
(C) 20 seconds
(D) 25 seconds
(E) 30 seconds
- When a train passes a lengthy object in "X+Y" seconds, it first covers the object’s length in "x" seconds, then its own length in the remaining "y" seconds.
- When a train passes a non-lengthy object like a tree/pole/person in "x" seconds, it passes it by covering its own length in "x" seconds.
What is the ratio between the times taken by a train of length 500 m to cross an electric pole and a bridge of length 400 m?
(A) 2:3
(B) 3:4
(C) 5:9
(D) 5:8
(E) 4:3
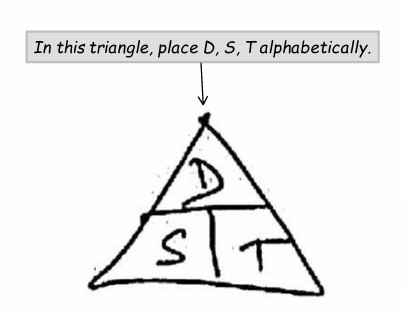
- When Speed is constant, Distance and Time are Directly Proportional
Formula: D = S × T (or) T = D / S - When Distance is constant, Speed and Time are Inversely Proportional
Formula: T = D / S (or) S = D / T - When Time is constant, Distance and Speed are Directly Proportional
Formula: D = S × T (or) S = D / T
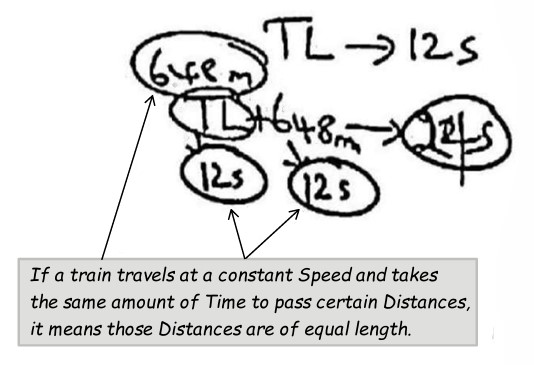
A train passes a signal pole and a bridge of length 648 m in 12 seconds and 24 seconds, respectively. What is the speed of the train?
(A) 186.4 km/hr
(B) 180 km/hr
(C) 179 km/hr
(D) 194.4 km/hr
(E) 134.8 km/hr
- If a train travels at a constant Speed and takes the same amount of Time to pass certain Distances, it means those Distances are of equal length.
A train of length 320 meters crosses a 400-meter platform in 40 seconds. If the train is running at 33.33% less than its usual speed, find the time taken by the train to cross a pole (approximately).
(A) 29 seconds
(B) 23 seconds
(C) 35 seconds
(D) 27 seconds
(E) 30 seconds
- To get P% of the Original Speed: New Speed = Original Speed × (P / 100).
- To get P% less than the Original Speed: New Speed = Original Speed × (1 - P/100).

The length of train A is 400 meters, and the length of train B is 'x' meters more than train A. If the speed of both train A and train B is equal and they cross a pole in 16 seconds and 24 seconds respectively, then in what time will train B cross a 400-meter-long platform?
(A) 32 sec
(B) 40 sec
(C) 45 sec
(D) 54 sec
(E) 24 sec
- If the question has the keyword "Equal/Same/Identical", start the sum by equating the corresponding quantities.