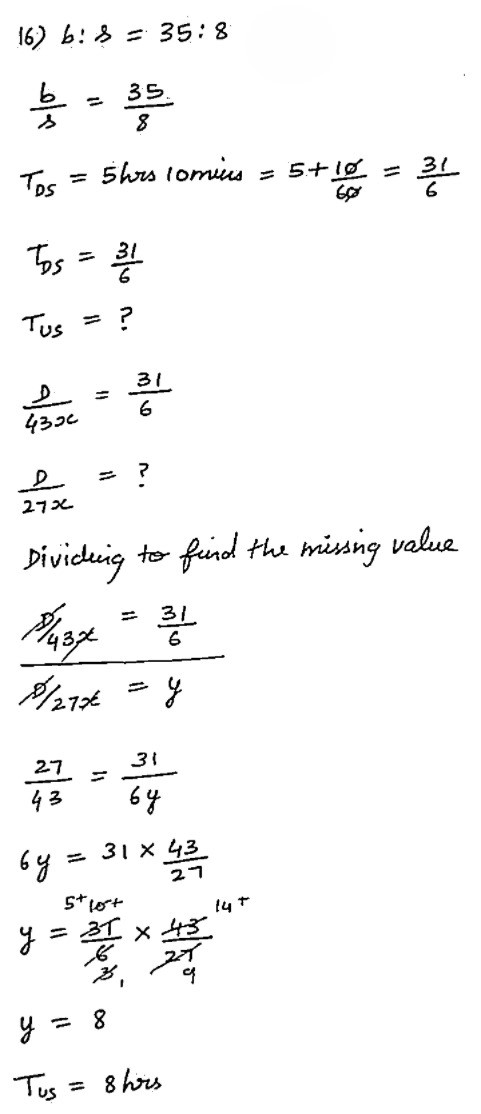📄 09 - Set-5 (Boats & Streams), p.1
📌 Speed Concepts
- The speed of the Boat is always greater than the speed of the Stream.
- Let:
- B → Speed of the Boat in Still Water
- S → Speed of the Stream
📌 Directional Keywords
- To identify Downstream or Upstream in questions, look for these keywords:
- Downstream → Same direction as stream
- Keywords: Same, Along, With the stream
- Upstream → Opposite direction to stream
- Keywords: Opposite, Against, Against the current
- Downstream → Same direction as stream
📌 Formulas
- Downstream Speed (DS) = B + S
- Upstream Speed (US) = B − S
🧩 Problems
The speed of a boat along and against the current is 22 km/hr and 18 km/hr respectively. Then the speed of the current (in km/hr) is:
(A) 4
(B) 2
(C) 7
(D) 3
- Speed along the current → Downstream Speed
- Speed against the current → Upstream Speed
A boy can swim in still water at a speed of 10 km/hr. If the speed of the current is 5 kmph, then the boy could swim 60 km downstream (along the flow) in how much time?
(A) 10 hours
==(B) 4 hours ==
(C) 5 hours
(D) 6 hours
- From the question here, "downstream" refers to the downstream speed.

A person can row 22(1/2) km an hour in still water and he finds that it takes him twice as long to row up as to row down the stream. The speed of the stream is:
==(A) 7(1/2) km/hr ==
(B) 13(1/2) km/hr
(C) 12 km/hr
(D) 3 km/hr
- The Time Ratio can be inversed to the Speed Ratio only when the Distance is constant.
- Upstream Distance is equal to Downstream Distance in this problem, so the Time Ratio can be inversed to the Speed Ratio for this problem.
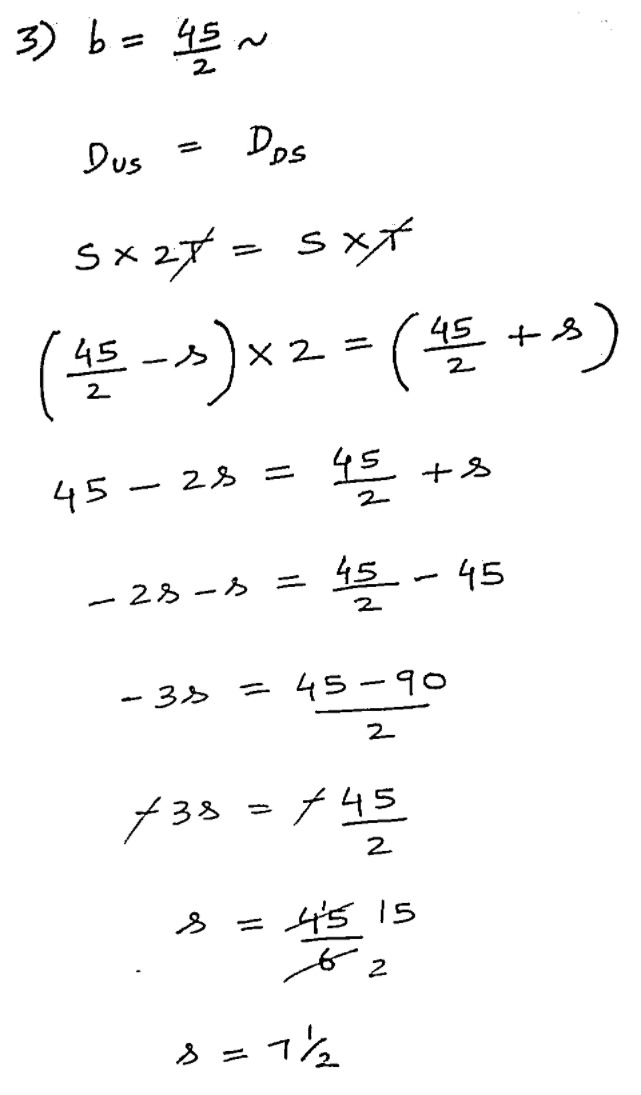
A boat goes 80 km upstream in 16 hours and 72 km downstream in 12 hours. The speed of the boat in still water is:
(A) 6.6 km/hour
(B) 7.5 km/hour
(C) 6.5 km/hour
(D) 5.5 km/hour
- In TDS questions, from the three quantities Time, Distance, and Speed, if any two are given in the question and one is missing, find the missing quantity first using the other two known quantities.
- From the question here, "upstream" refers to the upstream speed, and "downstream" refers to the downstream speed.

If the speed of a boat moving against the current is 18 km/hr, what is the speed of the stream if the boat's speed downstream is 50% greater than its speed upstream?
(A) 5.2 kmph
(B) 4.5 kmph
(C) 4.8 kmph
(D) 4.6 kmph
Upstream Speed.
- In percentage comparisons, the original value is always treated as 100% by default.
- The original is already considered 100%, and since the question says “50% greater,” we add 50% more to it, making it 150% in total.
A boat goes 20 km upstream and 44 km downstream in 8 hours. In 5 hours, it goes 15 km upstream and 22 km downstream. Determine the speed of the boat in still water:
(A) 6 km/h
(B) 10 km/h
(C) 8 km/h
(D) 7 km/h
- When two cases (upstream case and downstream case) along with their respective Time values are given in the question, start the sum with Time.
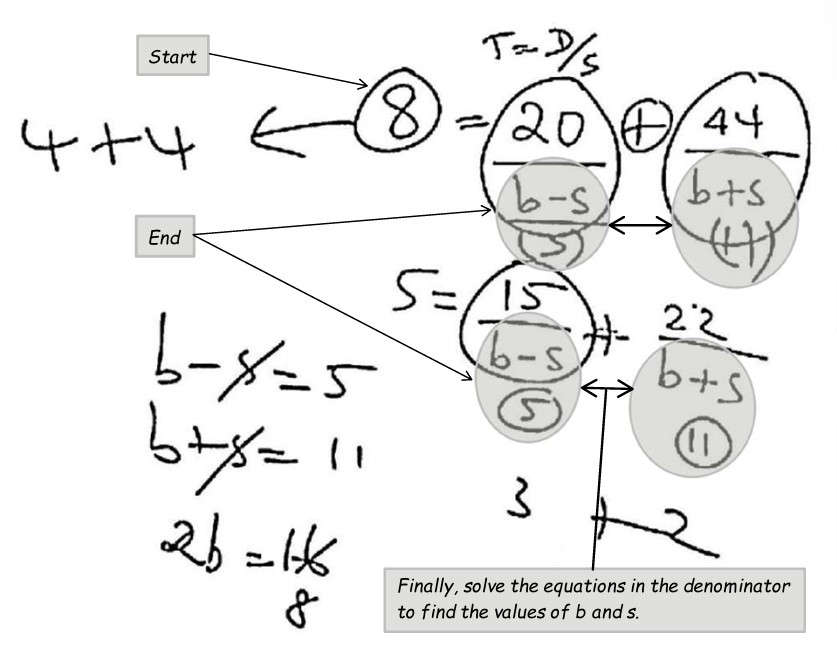
💡 Sample Value Substitution Method:
- If the options contain only whole numbers without fractions/decimals, and if the Time value on the LHS can be split properly or split equally, then solve the equations using the Sample Value Substitution Method.
- Start with the equation that has the smaller total time value, or one that can be split equally.
- Try values for the denominators (b+s and b-s) that make both sides of the equation balance correctly.
- Always ensure that the value of b+s is greater than the value of b-s.
- Finally, solve the two equations b + s = ... and b - s = ... to find the values of b and s.
💡 Reciprocal Substitution Method:
- If the options contain fractions/decimals, or if the Time value on the LHS cannot be split properly or split equally, then solve the equations using the Reciprocal Substitution Method.
- Let u = 1/b-s and d = 1/b+s
- Rewrite the original Time equations in terms of u and d to eliminate complex fractions.
- Solve the new equations to find the value of u and d.
- Then, take reciprocals of u and d to find the actual speeds 1/u = b-s and 1/d = b+s.
- Finally, solve the two equations b+s = ... and b-s = ... to find the values of b and s.
A motorboat whose speed is 20 km/h in still water takes 30 minutes more to go 24 km upstream than to cover the same distance downstream. If the speed of the boat in still water is increased by 2 km/h, then how much time will it take to go 30 km downstream and 30 km upstream?
(A) 2 hours 50 minutes
(B) 3 hours 10 minutes
(C) 3 hours 40 minutes
(D) 2 hours 40 minutes
- The Time taken for the boat to travel upstream will always be greater than the Time taken for the boat to travel downstream when covering the same distance.
- To solve equations involving the addition or subtraction of two fractions with a single unknown in either the numerators or the denominators, you can find the value of the unknown variable 's' by substituting appropriate even or odd values and checking whether the L.H.S. = R.H.S.
- The Time taken for the boat to travel upstream will always be greater than the Time taken for the boat to travel downstream when covering the same Distance.

A swimmer swims from a point P against the current for 6 minutes and then swims back along the current for the next 6 minutes and reaches a point Q. If the distance between P and Q is 120 meters, then the speed of the current (in km/h) is:
(A) 0.4
(B) 0.2
(C) 1
(D) 0.6
- In Boats and Streams, when asked to find the Speed, we cannot use the basic Speed formula S = D/T because the boat travels either upstream or downstream. So, either use the upstream or downstream formula.
A man rows a boat a certain distance downstream in 9 hours, while it takes 18 hours to row the same distance upstream. How many hours will it take him to row three-fifth of the same distance in still water?
(A) 9.5
==(B) 7.2 ==
(C) 10
(D) 12
- If the question has multiple Speed values or Time values along with the "Same Distance" keyword, assume the Distance to be the LCM of those Speeds or Times. This is because, according to the formula D = S × T, the Distance must be a common multiple of the given Speeds or Times.
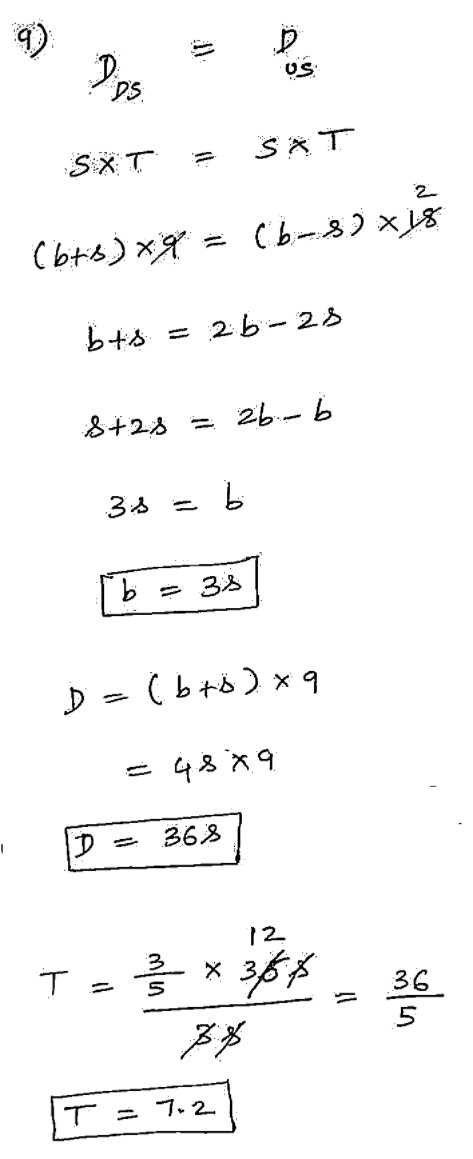
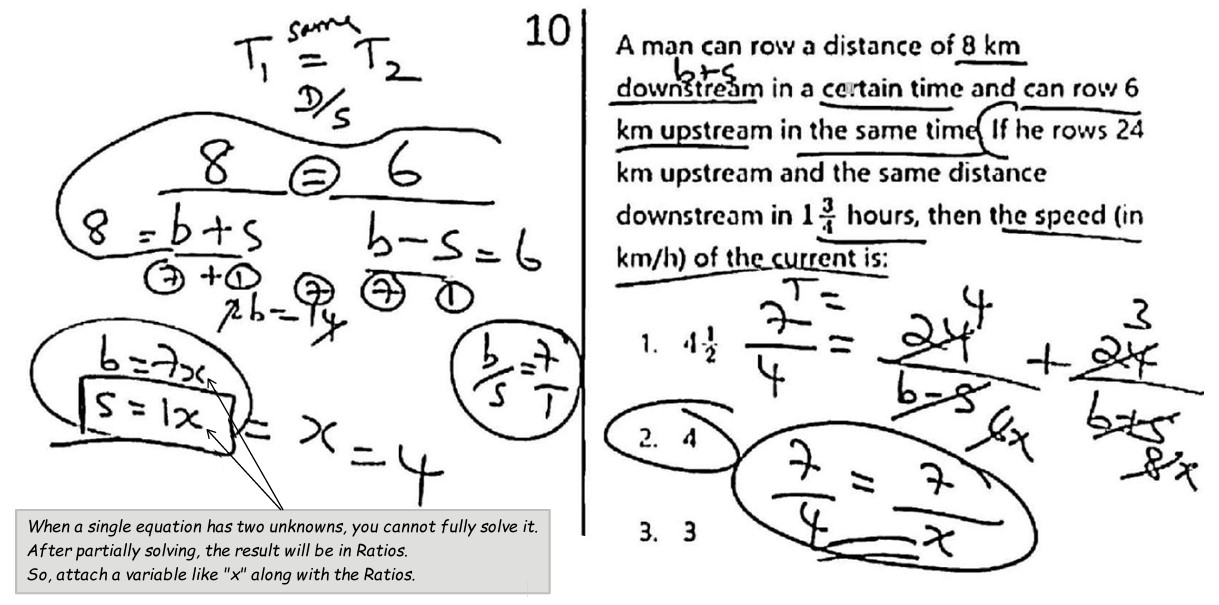
A man can row a distance of 8 km downstream in a certain time and can row 6 km upstream in the same time. If he rows 24 km upstream and the same distance downstream in 1(3/4) hours, then the speed (in km/h) of the current is:
(A) 4(1/2)
==(B) 4 ==
(C) 3
(D) 2(1/2)
- When you have two fractions set equal to each other (a proportion), use cross multiplication to eliminate the denominators and find the unknown values of the variables.
- When you have two fractions set equal to each other (a proportion), you can simplify the equation by canceling common factors shared by the numerators, the denominators, or a numerator and denominator on the same side of the equation (LHS or RHS).
- When a single equation has two unknowns, you cannot fully solve it. After partially solving, the result will be in Ratios. So, attach a variable like "x" along with the Ratios.
A boat can go 16 km downstream and 10 km upstream in 3 hours. It can also go 24 km downstream and 5 km upstream in 2 hours. In how much time (in hours) will it cover a distance of 64 km downstream?
(A) 5 hrs
(B) 6 hrs
==(C) 2 hrs ==
(D) 3 hrs
💡 Reciprocal Substitution Method:
- If the options contain fractions/decimals, or if the Time value on the LHS cannot be split properly or split equally, then solve the equations using the Reciprocal Substitution Method.
- Let u = 1/b-s and d = 1/b+s
- Rewrite the original Time equations in terms of u and d to eliminate complex fractions.
- Solve the new equations to find the value of u and d.
- Then, take reciprocals of u and d to find the actual speeds 1/u = b-s and 1/d = b+s.
- Finally, solve the two equations b+s = ... and b-s = ... to find the values of b and s.
X, Y are two points in a river. Points P and Q divide the straight line XY into three equal parts. The river flows along XY and the time taken by a boat to row from X to Q and from Y to Q are in the ratio 4:5. The ratio of the speed of the boat downstream to that of the river current is equal to:
(A) 4:3
==(B) 10:3 ==
(C) 3:10
(D) 13:5
- The Time Ratio can be inversed to the Speed Ratio only when the Distance is constant.
- Upstream Distance is not equal to Downstream Distance in this problem, so the Time Ratio cannot be inversed to the Speed Ratio for this problem.
A boat can go 3 km upstream and 5 km downstream in 55 minutes. It can also go 4 km upstream and 9 km downstream in 1 hour 25 minutes. In how much time (in hours) will it go 43.2 km downstream?
(A) 4.4
(B) 4.8
==(C) 3.6 ==
(D) 5.4
💡 Reciprocal Substitution Method:
- If the options contain fractions/decimals, or if the Time value on the LHS cannot be split properly or split equally, then solve the equations using the Reciprocal Substitution Method.
- Let u = 1/b-s and d = 1/b+s
- Rewrite the original Time equations in terms of u and d to eliminate complex fractions.
- Solve the new equations to find the value of u and d.
- Then, take reciprocals of u and d to find the actual speeds 1/u = b-s and 1/d = b+s.
- Finally, solve the two equations b+s = ... and b-s = ... to find the values of b and s.
A man rows from A to B (upstream) and A (downstream) in 12 hours. The distance between A and B is 240 km. The time taken by the man to row 6 km downstream is identical to the time taken by him to row 4 km upstream. What is the speed of the stream?
(A) 35/3 km/h
(B) 25/3 km/h
(C) 40/3 km/h
(D) 50/3 km/h
- If the question has the keyword "Equal/Same/Identical", start the sum by equating the corresponding quantities.
- When you have two fractions set equal to each other (a proportion), use cross multiplication to eliminate the denominators and find the unknown values of the variables.
- When you have two fractions set equal to each other (a proportion), you can simplify the equation by canceling common factors shared by the numerators, the denominators, or a numerator and denominator on the same side of the equation (LHS or RHS).
- When a single equation has two unknowns, you cannot fully solve it. After partially solving, the result will be in Ratios. So, attach a variable like "x" along with the Ratios.
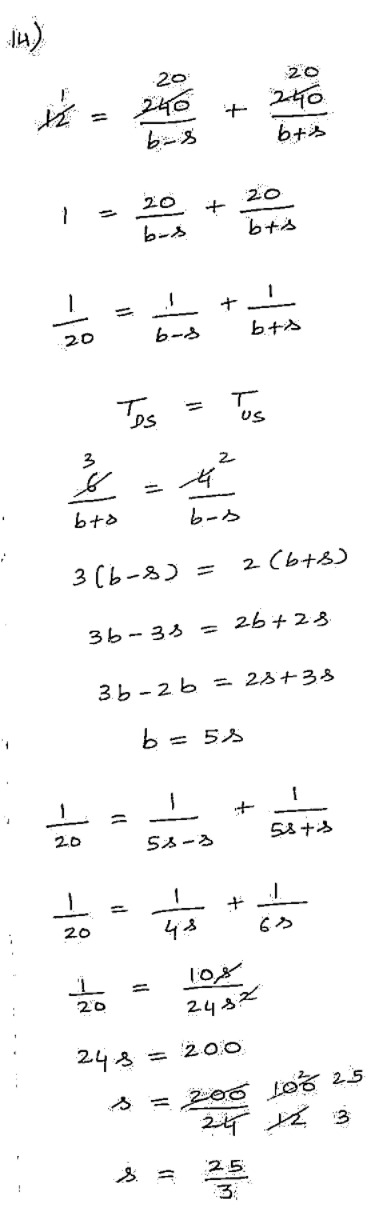
A man can row 7.5 km/h in still water. If the speed of the current is 2.5 km/h, it takes 3 hours more upstream than downstream for the same distance. The distance is:
(A) 37.5 km
(B) 27 km
(C) 35 km
(D) 30 km
- Distance is being directly asked here, so we can't assume the Distance value by taking the LCM of those Speed values for the "Same Distance" keyword.
- If the question says it takes 'x' hours more or less time in one direction than the other direction to cover the same Distance, use the Time difference equation to solve the problem.
- If the question has the keyword "Equal/Same/Identical", start the sum by equating the corresponding quantities.
!300
🧩 Test Yourself
The speed of a boat in still water is 18 km/h and the speed of the stream is 3 km/h. How much time (in hours) will it take to cover a distance of 105 km in downstream and in coming back?
==(A) 12 ==
(B) 10
(C) 15
(D) 9
A boat can go 54 km upstream in 6 hours. If the speed of the stream is 4.8 km/h, then how much time (in hours) will the boat take to cover a distance of 279 km downstream?
(A) 20
==(B) 15 ==
(C) 18
(D) 16
- In TDS questions, from the three quantities Time, Distance, and Speed, if any two are given in the question and one is missing, find the missing quantity first using the other two known quantities.
- From the question, "upstream" refers to the upstream speed.
A boatman goes 2 km against the current of the stream in 1 hour and goes 1 km along with the current in 10 minutes. How long will it take to go 6 km in stationary water?
==(A) 1 hr 30 mins ==
(B) 1 hr 15 mins
(C) 2 hr 30 mins
(D) 1 hr 45 mins
- The circled parts denote the Upstream Speed and Downstream Speed.
- In TDS questions, from the three quantities Time, Distance, and Speed, if any two are given in the question and one is missing, find the missing quantity first using the other two known quantities.
A boat can travel 78 km upstream and back in a total of 32 hours. It can travel 115 km upstream and 52 km downstream in a total of 19 hours. How much distance will the boat cover in 12 hours in still water?
(A) 92 km
==(B) 96 km ==
(C) 104 km
(D) 100 km
A boatman rows to a place 30 km distance and back in 14 hours. He finds that he can row 10 km with the stream at the same time as 4 km against the stream. Find the speed (in km/h) of the stream.
(A) 9/2
==(B) 9/4 ==
(C) 2/9
(D) 4/9
💡 Sample Value Substitution Method:
- If the options contain only whole numbers without fractions/decimals, and if the Time value on the LHS can be split properly or split equally, then solve the equations using the Sample Value Substitution Method.
- Start with the equation that has the smaller total time value, or one that can be split equally.
- Try values for the denominators (b+s and b-s) that make both sides of the equation balance correctly.
- Always ensure that the value of b+s is greater than the value of b-s.
- Finally, solve the two equations b + s = ... and b - s = ... to find the values of b and s.
A motorboat takes 18 hours to go downstream, and it takes 36 hours to return the same distance. Find the ratio of the speed of the boat in still water to the speed of the stream.
(A) 3:1
(B) 2:3
(C) 2:1
(D) 3:2
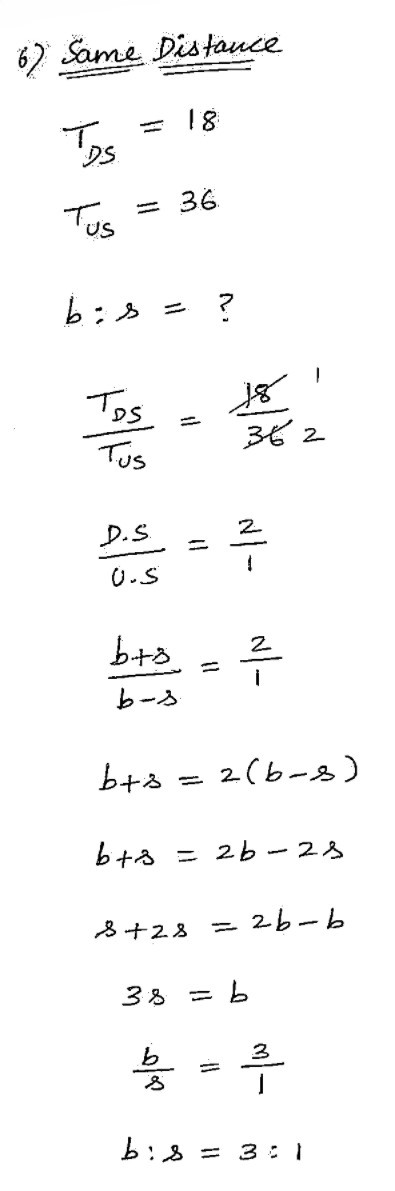
A motorboat travelling at a certain speed can cover a distance of 24 km upstream and 40 km downstream in 17 hours. At the same speed it can travel 32 km downstream and 12 km upstream in 10 hours. What is the speed of the current?
(A) 5 km/h
(B) 4 km/h
(C) 2 km/h
(D) 3 km/h
💡 Sample Value Substitution Method:
- If the options contain only whole numbers without fractions/decimals, and if the Time value on the LHS can be split properly or split equally, then solve the equations using the Sample Value Substitution Method.
- Start with the equation that has the smaller total time value, or one that can be split equally.
- Try values for the denominators (b+s and b-s) that make both sides of the equation balance correctly.
- Always ensure that the value of b+s is greater than the value of b-s.
- Finally, solve the two equations b + s = ... and b - s = ... to find the values of b and s.
A man can row a distance of 6 km in 1 hour in still water. He can row the same distance in 45 minutes with the current. Find the total time taken by him to row a distance of 16 km with the current and to return to the starting point.
(A) 4 hrs 40 mins
==(B) 6 hrs ==
(C) 4 hrs
(D) 6 hrs 40 mins
- In TDS questions, from the three quantities Time, Distance, and Speed, if any two are given in the question and one is missing, find the missing quantity first using the other two known quantities.
A motorboat, whose speed in 15 km/h in still water, goes 50 km downstream and comes back in a total of 7 hours 30 minutes. The speed of the stream (in km/h) is:
(A) 9 km/h
(B) 5 km/h
(C) 11 km/h
(D) 7 km/h
💡 Sample Value Substitution Method:
- If the options contain only whole numbers without fractions/decimals, and if the Time value on the LHS can be split properly or split equally, then solve the equations using the Sample Value Substitution Method.
- Start with the equation that has the smaller total time value, or one that can be split equally.
- Try values for the denominators (b+s and b-s) that make both sides of the equation balance correctly.
- Always ensure that the value of b+s is greater than the value of b-s.
- Finally, solve the two equations b + s = ... and b - s = ... to find the values of b and s.
A boat covers a distance of 55 km downstream in 5 hours, while it takes 11 hours to cover the same distance upstream. What is the speed of the boat?
==(A) 8 km/h ==
(B) 9 km/h
(C) 11 km/h
(D) 7 km/h
- In TDS questions, from the three quantities Time, Distance, and Speed, if any two are given in the question and one is missing, find the missing quantity first using the other two known quantities.
A boatman rows 2 km in 10 mins, along the stream and 12 km in 2 hours against the stream. What is the speed of the stream?
==(A) 3 km/h ==
(B) 2.5 km/h
(C) 4 km/h
(D) 3.5 km/h
- In TDS questions, from the three quantities Time, Distance, and Speed, if any two are given in the question and one is missing, find the missing quantity first using the other two known quantities.
A boat covers 24 km upstream and 36 km downstream in 10 hours, and 36 km upstream and 24 km downstream in 12 hours. The speed of the current is:
(A) 26/9 km/h
(B) 33/13 km/h
(C) 25/8 km/h
(D) 24/7 km/h
💡 Reciprocal Substitution Method:
- If the options contain fractions/decimals, or if the Time value on the LHS cannot be split properly or split equally, then solve the equations using the Reciprocal Substitution Method.
- Let u = 1/b-s and d = 1/b+s
- Rewrite the original Time equations in terms of u and d to eliminate complex fractions.
- Solve the new equations to find the value of u and d.
- Then, take reciprocals of u and d to find the actual speeds 1/u = b-s and 1/d = b+s.
- Finally, solve the two equations b+s = ... and b-s = ... to find the values of b and s.
A boat can travel 16.9 km downstream in 52 min. If the speed of the current is 3 km/h, then how much time (in hours) will the boat take to travel 84 km upstream?
(A) 6
(B) 13.5
==(C) 6.22 ==
(D) 7.5
- In TDS questions, from the three quantities Time, Distance, and Speed, if any two are given in the question and one is missing, find the missing quantity first using the other two known quantities.
A man rows 48 km and back in 48 hours. He can row 4 km with the stream in the same time as 3 km against the stream. The speed of the stream (in km/h) is:
(A) 5/21
(B) 7/21
==(C) 7/24 ==
(D) 3/29
💡 Reciprocal Substitution Method:
- If the options contain fractions/decimals, or if the Time value on the LHS cannot be split properly or split equally, then solve the equations using the Reciprocal Substitution Method.
- Let u = 1/b-s and d = 1/b+s
- Rewrite the original Time equations in terms of u and d to eliminate complex fractions.
- Solve the new equations to find the value of u and d.
- Then, take reciprocals of u and d to find the actual speeds 1/u = b-s and 1/d = b+s.
- Finally, solve the two equations b+s = ... and b-s = ... to find the values of b and s.
The ratio of the speed of a boat to that of the current water is 35 : 8. The boat goes along with the current in 5 hours 10 minutes. What will be the time taken by the boat to come back?
(A) 5 hours 15 minutes 58 seconds
(B) 6 hours 45 minutes 10 seconds
(C) 8 hours 13 minutes 48 seconds
- The Speed Ratio can be inversed to the Time Ratio only when the Distance is constant.
- Upstream Distance is equal to Downstream Distance in this problem, so the Speed Ratio can be inversed to the Time Ratio for this problem.
✅ Rounding Rule:
- If the number after the decimal point is 5 or more → Round up to the next whole number.
- If the number after the decimal point is less than 5 → Round down to the same whole number.